Picture from : RepRap Blog
Thursday, January 20, 2011
Zero positioning, new ideas
Lately I have been working on mounting an Open Source 3D printer called RepRap(Version 1.0, Darwin). While working on it, I learnt about their brilliant idea for Zero Positioning. They use a tiny beam light sensor(Opto endstop V2.1) which is interrupted by a small stick which is connected to the moving joint. The interrupted state defines that the moving joint is in the zero position.
Saturday, January 15, 2011
What is EEPROM / E2PROM ?
We do need a way to save the numbers which represents the current situation of the robot actuators somewhere(either at PC or somewhere on Arduino microcontroller, EEPROM here). This post dedicates itself to storing data on Arduino non-volatile memory and use this information for zero positioning of the moving joint. First an introduction to EEPROM from Wikipedia and later code example and links to its API's at Arduino website.
What is EEPROM ?
EEPROM (also written E2PROM and pronounced "e-e-prom," "double-e prom" or simply "e-squared") stands for Electrically Erasable Programmable Read-Only Memory and is a type ofnon-volatile memory used in computers and other electronic devices to store small amounts of data that must be saved when power is removed, e.g., calibration tables or device configuration.
What is EEPROM ?
EEPROM (also written E2PROM and pronounced "e-e-prom," "double-e prom" or simply "e-squared") stands for Electrically Erasable Programmable Read-Only Memory and is a type ofnon-volatile memory used in computers and other electronic devices to store small amounts of data that must be saved when power is removed, e.g., calibration tables or device configuration.
When larger amounts of static data are to be stored (such as in USB flash drives) a specific type of EEPROM such as flash memory is more economical than traditional EEPROM devices. EEPROMs are realized as arrays of floating-gate transistors.
EEPROM is user-modifiable read-only memory (ROM) that can be erased and reprogrammed (written to) repeatedly through the application of higher than normal electrical voltage generated externally or internally in the case of modern EEPROMs. EPROM usually must be removed from the device for erasing and programming, whereas EEPROMs can be programmed and erased in circuit. Originally, EEPROMs were limited to single byte operations which made them slower, but modern EEPROMs allow multi-byte page operations. It also has a limited life - that is, the number of times it could be reprogrammed was limited to tens or hundreds of thousands of times. That limitation has been extended to a million write operations in modern EEPROMs. In an EEPROM that is frequently reprogrammed while the computer is in use, the life of the EEPROM can be an important design consideration. It is for this reason that EEPROMs were used for configuration information, rather than random access memory.*
Practical Information about how to get things to work :
- http://www.arduino.cc/playground/Main/InterfacingWithHardware#Storage
- http://arduino.cc/en/Reference/EEPROMWrite
Source Code :
#include EEPROM.h
int a = 0;
int value;
void setup()
{
Serial.begin(9600);
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++){
Serial.println("***");
EEPROM.write(i, i);
}
}
void loop()
{
value = EEPROM.read(a);
Serial.print(a);
Serial.print("\t");
Serial.print(value);
Serial.println("***");
a++;
if (a == 20){
a = 0;
Serial.println("DONE");
delay(5000000);
}
}
* : Source : Wikipedia
Thursday, January 13, 2011
Problem of current position in case of loosing power & possible fixes ...
I think I have found my way to bear in mind the current position of the robot in case of the robot loosing power & not being able to drive itself back to the ZERO. The way is to either use the built in EEPROM(512 bytes), or other external storages which can be connected to Arduino. More info about EEPROM :
The 2nd option is to always send the position to the computer and save it somewhere there at the program(Lots of traffic on serial port, higher risk to encounter problem or missing packages).
Too tiered to fix it now ... Later ...
The 2nd option is to always send the position to the computer and save it somewhere there at the program(Lots of traffic on serial port, higher risk to encounter problem or missing packages).
Too tiered to fix it now ... Later ...
It matters to choose BYTE or INTEGER, BUG fixed + Handshaked protocol added
Just now fixed a bug in my code. Choosing BYTE as my variable type made some confusions on startup for the program as it couldn't initialize the variable with 0 value. The problem was fixed as soon as I changed the type to INTEGER. This resulted in errors in my program as no value made some random cases to launch which was totally wrong. This means that the bug on startup of my program which I talked to my supervisor today about is fixed :-) I was thinking as it just happened on startup to be a noise or some wrong reading from ports on Arduino, but it seems to be just a confusion on defining the variable as byte !!! I have also changed the startup value from 0 to -1 which result in no possible meaningful combination ...
Differences with previous code : Handshake added, Startup bug fixed, Some changes in standard writing to serial port from Arduino side.
Differences with previous code : Handshake added, Startup bug fixed, Some changes in standard writing to serial port from Arduino side.
//the code is entering saving with Java and we are printing as little as possible in Serial ports
// Encoders inputs
byte pinEncA[] = {7,5,3}; // digital inputs
byte pinEncB[] = {6,4,2}; // digital inputs
// MOTOR OUTPUTS
byte pinDir[] = {13,8,12}; // digital output, controls direction for motor nr. [x]
byte pinPwm[] = {10,11,9}; // analog output, controls motor speed, nr. [x]
//Global variables
int readValue;
int pwmValue;
int motorDir;
//int channelA = 2;
//int channelB = 3;
int cycle[] = {0, 0, 0};
boolean f = false, b = false, r = false, l = false;
int cyclecounter[] = {0, 0, 0};
int cyclecounterold[] = {0, 0, 0};
//13 , 10 right, down
//8 , 11 middle, top
//9, 12 left, down
void setup(){
Serial.begin(115200);
Serial.println("WELCOME TO C1S0");
for (int i=0; i < 3; i++){
pinMode(pinDir[i], OUTPUT);
pinMode(pinPwm[i], OUTPUT);
//in case, just to be sure ...
digitalWrite(pinPwm[i], LOW);
// just in case to be sure
digitalWrite(pinDir[i], LOW);
pinMode(pinEncA[i], INPUT);
pinMode(pinEncB[i], INPUT);
digitalWrite(pinEncA[i], LOW);
digitalWrite(pinEncB[i], LOW);
cyclecounter[i] = -1;
cyclecounterold[i] = -1;
}//end of for
}//end of setup()
void loop(){
commandCenter();
checkEncoder();
}//end of loop
void commandCenter(){
//variables
int temp = 0;
if ( Serial.available() > 0 ){
readValue = Serial.read();
switch (readValue){
case 'h' : //handshake
Serial.println("h");
break;
case '0' ://motor #0
int temp__;
temp__ = 0;
if(Serial.available() < 0)
;
delay(500);
temp__ = Serial.read();
if (temp__ == 102){// -f -> forward
Serial.println("*** Right forward ***");
digitalWrite(pinDir[0], LOW);
digitalWrite(pinPwm[0], HIGH);
}//end of if
else if(temp__ == 98){// -b -> backward
Serial.println("*** Right backward ***");
digitalWrite(pinDir[0], HIGH);
digitalWrite(pinPwm[0], HIGH);
}
else{
Serial.print("error ");
Serial.println(temp__);
}
f = false;
b = false;
l = false;
r = true;
break;
case '1' ://motor #1
int temp_;
if(Serial.available() < 1)
;
delay(500);
temp_ = Serial.read();
if (temp_ == 102){// -f
Serial.println("*1FW*");
digitalWrite(pinDir[1], LOW);
digitalWrite(pinPwm[1], HIGH);
}//end of if
else if(temp_ == 98){// -b
Serial.println("*1BW*");
digitalWrite(pinDir[1], HIGH);
digitalWrite(pinPwm[1], HIGH);
}
else{
Serial.print("error ");
Serial.println(temp_);
}
f = true;
b = false;
l = false;
r = false;
break;
case '2' ://l -> left
temp_ = 0;
if(Serial.available() < 1)
;
delay(500);
temp_ = Serial.read();
if (temp_ == 102){//motor #2
Serial.println("*2FW*");
digitalWrite(pinDir[2], LOW);
digitalWrite(pinPwm[2], HIGH);
}//end of if
else if(temp_ == 98){// -b
Serial.println("*2BW*");
digitalWrite(pinDir[2], HIGH);
digitalWrite(pinPwm[2], HIGH);
}
else{
Serial.print("error ");
Serial.println(temp_);
}
f = false;
b = false;
l = true;
r = false;
break;
case 82 : //R->RESET
Serial.println("*** Resetting ***");
for (int i=0; i < 3; i++){
digitalWrite(pinPwm[i], LOW);//Setting all PWM's to LOW
Serial.print("C");
Serial.print(i);
Serial.print("=");
Serial.println(cycle[i]);
}//end of for
f = false;
b = false;
l = false;
r = false;
break;
}//end of switch
}
/*
if (f || b || r || l){
Serial.print("cycle[i]: ");
Serial.println(cycle[i]);
}//end of if
*/
}//end of commandCenter
//int angleMaalt;
void checkEncoder(){
int A;
int B;
int i;
for (i = 0; i < 3; i++){
A = digitalRead(pinEncA[i]);
B = digitalRead(pinEncB[i]);
if ( (A==LOW) && (B==LOW) )
cyclecounter[i] = 0;
else if ( (A==LOW) && (B==HIGH) )
cyclecounter[i] = 1;
else if ( (A==HIGH) && (B==HIGH) )
cyclecounter[i] = 2;
else if ( (A==HIGH) && (B==LOW) )
cyclecounter[i] = 3;
switch (cyclecounter[i]){
case (0) : {
if ( cyclecounterold[i] == 0){
;//Do nothing
}
else if ( cyclecounterold[i] == 1){
cycle[i]++;
Serial.print("C");
Serial.print(i);
Serial.print("-");
Serial.println(cycle[i]);
}
else if ( cyclecounterold[i] == 2){
Serial.println("Error reading from Encoder-");
}
else if ( cyclecounterold[i] == 3){
cycle[i]--;
Serial.print("C");
Serial.print(i);
Serial.print("-");
Serial.println(cycle[i]);
}
else
;//Serial.print("ERROR");
break;
}//end of case-0
case (1) : {
if ( cyclecounterold[i] == 0){
cycle[i]++;
Serial.print("C");
Serial.print(i);
Serial.print("-");
Serial.println(cycle[i]);
}
if ( cyclecounterold[i] == 2){
cycle[i]--;
Serial.print("C");
Serial.print(i);
Serial.print("-");
Serial.println(cycle[i]);
}
else if ( cyclecounterold[i] == 3){
Serial.println("Error reading from Encoder--");
}
else
;//Serial.print("ERROR");
break;
}
case (2) : {
if ( cyclecounterold[i] == 1){
cycle[i]--;
Serial.print("C");
Serial.print(i);
Serial.print("-");
Serial.println(cycle[i]);
}
else if ( cyclecounterold[i] == 2)
;
else if ( cyclecounterold[i] == 3){
cycle[i]++;
Serial.print("C");
Serial.print(i);
Serial.print("-");
Serial.println(cycle[i]);
}
else if ( cyclecounterold[i] == 0){
Serial.println("Error reading from Encoder---");
}
else
;//Serial.print("ERROR");
break;
}//end of case-2
case(3) : {
if (cyclecounterold[i] == 0){
cycle[i]--;
Serial.print("C");
Serial.print(i);
Serial.print("-");
Serial.println(cycle[i]);
}
else if (cyclecounterold[i] == 1){
Serial.println("Error reading from Encoder----");
}
else if ( cyclecounterold[i] == 2){
cycle[i]++;
Serial.print("C");
Serial.print(i);
Serial.print("-");
Serial.println(cycle[i]);
}
else if ( cyclecounterold[i] == 3)
;
else
;//Serial.print("ERROR");
break;
}//end of case-3
}
cyclecounterold[i] = cyclecounter[i];
}//end of for
}//end of checkEncoder()
Wednesday, January 12, 2011
Meeting with my supervisor Mats Høvin, Summary
Today I met my supervisor Mats Høvin(associated professor at IFI,UiO). Here comes a summary of what he thinks I should be focusing on :

- Handshake protocol. I do not have this protocol & this is something that according to Mats, I better have it implemented in my code
- Zero Positioning. My suggestion to this challenge is to save the current position all the time either at PC side or at the Arduino non-volatile memory.
- Sending data packages back & forth in serial communication would possibly result in loss of data packages. How can my code handle this kind of problems ?
- Error on startup, fix for it ? Is it a programming error, or a hardware error because of Noise on reading inputs from ports ???
- Sending many bytes and the delays resulting by that
- The speed control, should be handled in java or Arduino ??? Maybe fast in the beginning and slow down little by little while reaching the end of the axle
- Play off modus & Should it be target based, or follow every detail from the log blindly ??? Discuss ...
- Camera candidates & streaming , but not image processing -> Intelligent cameras with output ports(how many???) for sending commands to Arduino according to the image processing done by camera itself.
- Using WiFi tech & how ??? WiFly component ?
- Programing a simulator in JAVA (xyz generation and visualization in JAVA)
- PHP/JAVA Applet GUI & Streaming show on website
- Multi Arduino card solutions ? Benefits and disadvantages ??? Discuss ...
- FPGA??? A possible solution instead of Arduino? Discuss ...
- Different methods to read data from encoders, External interruptions or software methods reading encoders value by analogRead() on loop frequence. Discuss based on Atmel/AVR architecture
- Positioning in the room & semi-Kinect sensors
Tuesday, January 11, 2011
Multi Arduino card solution ?
Discussion about using more than one Arduino card in this project on Arduino.cc froum
http://www.arduino.cc/cgi-bin/yabb2/YaBB.pl?num=1294709114/
http://www.arduino.cc/cgi-bin/yabb2/YaBB.pl?num=1294709114/
Friday, January 7, 2011
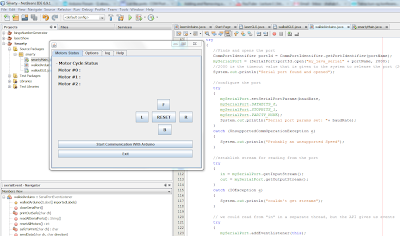
Robot foot Control Panel(in Java) for the robot feet, version 0.01
This is the first snapshot of a GUI for the Robot foot Control Panel in Java that I am designing right now. I do not have much trouble with it and it looks promissing :-) Updates of the code and more snapshots come soon ...
Serial data transmission and problem with it being SLOW !!!
A while ago I was facing a problem reading some inputs from Serial Communication(USB port) in Arduino. The Arduino would work perfect(read all the inputs from Serial Communication Window as planned) if I was having my debug print outs but not if I would remove them(they also could be substituted by Delays) !!! I later tried to find out about them and here was the answer :
"Serial data transmission is slow. The Serial.print statement takes time, which allows time for more data to arrive. You have two choices. Add a delay statement to the while loop, and hope all the data arrives in time is the first choice. The longer you waste time waiting for data, the better your chances of it all arriving in time.
The second choice is to add an end-of-packet marker, and keep appending to temp until that end of packet marker arrives. Only use the data in temp when the end of packet marker has arrived.Source : http://www.arduino.cc/cgi-bin/yabb2/YaBB.pl?num=1294185714/1#1
The delay masks the issue of not being able to read a complete packet in one pass. If the delay is too small, the whole packet will not arrive before the delay(s) expire. If the delay is too large, you are just wasting time.
The better approach is to add an end of packet marker to the packer, wo you can read the packet as quickly as possible.."
RxTx API, Java
By clicking on the following link you can have access to the full directory of RxTx library API's in Java :
Thursday, January 6, 2011
Encoders & Cycles 2, All DC motors are monitored now -> All_Encoders.pde
This code can monitor the changes in cycles of all the DC motors used in the robot feet.
// Encoders inputs
byte pinEncA[] = {7,5,3}; // digital inputs
byte pinEncB[] = {6,4,2}; // digital inputs
// MOTOR OUTPUTS
byte pinDir[] = {13,8,12}; // digital output, controls direction for motor nr. [x]
byte pinPwm[] = {10,11,9}; // analog output, controls motor speed, nr. [x]
//Global variables
int readValue;
int pwmValue;
int motorDir;
//int channelA = 2;
//int channelB = 3;
int cycle[] = {0, 0, 0};
boolean f = false, b = false, r = false, l = false;
byte cyclecounter[] = {0, 0, 0};
byte cyclecounterold[] = {0, 0, 0};
//13 , 10 right, down
//8 , 11 middle, top
//9, 12 left, down
void setup(){
Serial.begin(9600);
Serial.println("WELCOME TO C1S0");
for (int i=0; i < 3; i++){
pinMode(pinDir[i], OUTPUT);
pinMode(pinPwm[i], OUTPUT);
//in case, just to be sure ...
digitalWrite(pinPwm[i], LOW);
// just in case to be sure
digitalWrite(pinDir[i], LOW);
pinMode(pinEncA[i], INPUT);
pinMode(pinEncB[i], INPUT);
digitalWrite(pinEncA[i], LOW);
digitalWrite(pinEncB[i], LOW);
cyclecounter[i] = 0;
cyclecounterold[i] = 0;
}//end of for
}//end of setup()
void loop(){
commandCenter();
checkEncoder();
}//end of loop
void commandCenter(){
//variables
int temp = 0;
if ( Serial.available() > 0 ){
readValue = Serial.read();
switch (readValue){
case 102 ://f -> forward
Serial.println("*** Forward ***");
digitalWrite(pinDir[1], LOW);
digitalWrite(pinPwm[1], HIGH);
f = true;
b = false;
l = false;
r = false;
break;
case 98 ://b -> back
Serial.println("*** Backward ***");
digitalWrite(pinDir[1], HIGH);
digitalWrite(pinPwm[1], HIGH);
f = false;
b = true;
l = false;
r = false;
break;
case 108 ://l -> left
int temp_;
temp_ = 0;
if(Serial.available() < 1)
;
delay(5);
temp_ = Serial.read();
if (temp_ == 102){// -f
Serial.println("*** Left forward ***");
digitalWrite(pinDir[2], LOW);
digitalWrite(pinPwm[2], HIGH);
}//end of if
else if(temp_ == 98){// -b
Serial.println("*** Left backward ***");
digitalWrite(pinDir[2], HIGH);
digitalWrite(pinPwm[2], HIGH);
}
else Serial.println("*** NOTHING ***");
f = false;
b = false;
l = true;
r = false;
break;
case 114 ://r -> right
int temp__;
temp__ = 0;
if(Serial.available() < 0)
;
delay(5);
temp__ = Serial.read();
if (temp__ == 102){// -f
Serial.println("*** Right forward ***");
digitalWrite(pinDir[0], LOW);
digitalWrite(pinPwm[0], HIGH);
}//end of if
else if(temp__ == 98){// -b
Serial.println("*** Right backward ***");
digitalWrite(pinDir[0], HIGH);
digitalWrite(pinPwm[0], HIGH);
}
f = false;
b = false;
l = false;
r = true;
break;
case 82 : //R->RESET
Serial.println("*** Resetting ***");
for (int i=0; i < 3; i++){
digitalWrite(pinPwm[i], LOW);//Setting all PWM's to LOW
Serial.print("*** Cycle[");
Serial.print(i);
Serial.print("] = ");
Serial.println(cycle[i]);
}//end of for
f = false;
b = false;
l = false;
r = false;
break;
}//end of switch
}
/*
if (f || b || r || l){
Serial.print("cycle[i]: ");
Serial.println(cycle[i]);
}//end of if
*/
}//end of commandCenter
//int angleMaalt;
void checkEncoder(){
int A;
int B;
int i;
for (i = 0; i < 3; i++){
A = digitalRead(pinEncA[i]);
B = digitalRead(pinEncB[i]);
if ( (A==LOW) && (B==LOW) )
cyclecounter[i] = 0;
else if ( (A==LOW) && (B==HIGH) )
cyclecounter[i] = 1;
else if ( (A==HIGH) && (B==HIGH) )
cyclecounter[i] = 2;
else if ( (A==HIGH) && (B==LOW) )
cyclecounter[i] = 3;
if (cyclecounter[i] == 0){
Serial.print("CAME IN AS 0");
if ( cyclecounterold[i] == 0){
Serial.print("Case old is 0");
}
else if ( cyclecounterold[i] == 3){
//angleMaalt++;
Serial.println(cycle[i]);
Serial.print("*** Changed cycle[");
Serial.print(i);
Serial.print("] = ");
cycle[i]--;
Serial.println(cycle[i]);
Serial.println("++++++");
Serial.print("cyccleCounter is : ");
Serial.println(cyclecounter[i]);
Serial.print("cyccleCounterOld is : ");
Serial.println(cyclecounterold[i]);
}
else if ( cyclecounterold[i] == 2){
Serial.println("Error reading from Encoder-");
Serial.println("cyclecounter[i]");
Serial.println(cyclecounter[i]);
Serial.println("cyclecounterold[i]");
Serial.println(cyclecounterold[i]);
}
else Serial.print("CRAP");
}
else if (cyclecounter[i] == 1){
/*if ( cyclecounterold[i] == 2)
angleMaalt--;
else if ( cyclecounterold[i] == 0)
angleMaalt++;
else*/ if ( cyclecounterold[i] == 3){
Serial.println("Error reading from Encoder--");
Serial.println("cyclecounter[i]");
Serial.println(cyclecounter[i]);
Serial.println("cyclecounterold[i]");
Serial.println(cyclecounterold[i]);
}
}
else if (cyclecounter[i] == 2){
/*if ( cyclecounterold[i] == 3)
angleMaalt--;
else if ( cyclecounterold[i] == 1)
angleMaalt++;
else*/ if ( cyclecounterold[i] == 0){
Serial.println("Error reading from Encoder---");
Serial.println("cyclecounter[i]");
Serial.println(cyclecounter[i]);
Serial.println("cyclecounterold[i]");
Serial.println(cyclecounterold[i]);
}
}
else if (cyclecounter[i] == 3){
if (cyclecounterold[i] == 0){
//angleMaalt--;
Serial.println(cycle[i]);
Serial.print("*** Changed cycle[");
Serial.print(i);
Serial.print("] = ");
cycle[i]++;
Serial.println(cycle[i]);
Serial.print("++++++");
Serial.print("cyccleCounter is : ");
Serial.println(cyclecounter[i]);
Serial.print("cyccleCounterOld is : ");
Serial.println(cyclecounterold[i]);
}
/*else if ( cyclecounterold[i] == 2)
angleMaalt++;*/
else if ( cyclecounterold[i] == 1){
Serial.println("Error reading from Encoder----");
Serial.println("cyclecounter[i]");
Serial.println(cyclecounter[i]);
Serial.println("cyclecounterold[i]");
Serial.println(cyclecounterold[i]);
}
}
cyclecounterold[i] = cyclecounter[i];
}//end of for
}//end of checkEncoder()
Wednesday, January 5, 2011
Encoders & Cycles
Tonight(or better say this morning at 4:00 a.m.) I managed to make a code to finally count the cycles(it takes around 70 cycles for a motor to screw totally open) that the light fork encoder on this foot counts. This code is an alpha version which monitors just one of the DC motors(the one in the middle, motor with index "1" in the code).
The challenge to discus here is a limitation in Arduino which I have discussed in my previous post here(few external interruption on Arduino ). Most Arduino boards, so do mine, have just two external interruptions and this makes me not to use this method(which looks to be a perfect one) to monitor the changes on the pins received from the motor driver(changes in A & B state from Motor driver which tells us about the current position of the DC motor connected to it). With external interruptions out of the picture the only way that I came to is to solve this with a software trick. I tried to monitor the changes sent from the encoder which is connected to a moving motors as fast as I can. This is done by placing readFromEncoder() method in loop() method which repeats pretty fast and up to now has given satisfactory results. Check the code down here :
// Encoders inputs
byte pinEncA[] = {7,5,3}; // digital inputs
byte pinEncB[] = {6,4,2}; // digital inputs
// MOTOR OUTPUTS
// digital output, controls direction for motor nr. [x]
byte pinDir[] = {13,8,12};
// analog output, controls motor speed, nr. [x]
byte pinPwm[] = {10,11,9};
//Global variables
int readValue;
int pwmValue;
int motorDir;
int cycle;
boolean f = false, b = false, r = false, l = false;
byte cycleCounter;
byte cycleCounterOld;
void setup(){
Serial.begin(9600);
Serial.println("WELCOME TO C1S0");
for (int i=0; i < 3; i++){
pinMode(pinDir[i], OUTPUT);
pinMode(pinPwm[i], OUTPUT);
//in case, just to be sure ...
digitalWrite(pinPwm[i], LOW);
//in case, just to be sure ...
digitalWrite(pinDir[i], LOW);
pinMode(pinEncA[i], INPUT);
pinMode(pinEncB[i], INPUT);
}//end of for
}//end of setup()
void loop(){
// digitalWrite(pinDir[2], LOW);
// digitalWrite(pinPwm[2], HIGH);
// Serial.println("...");
//if ( Serial.available() > 0 )
commandCenter();
readFromEncoder();
//Serial.print("cycle: ");
//Serial.println(cycle);
}//end of loop
void commandCenter(){
//variables
int temp = 0;
// while (Serial.available() < 0)
// ;
if ( Serial.available() > 0 ){
readValue = Serial.read();
switch (readValue){
case 102 ://f -> forward
Serial.println("*** Forward ***");
digitalWrite(pinDir[1], LOW);
digitalWrite(pinPwm[1], HIGH);
f = true;
b = false;
l = false;
r = false;
break;
case 98 ://b -> back
Serial.println("*** Backward ***");
digitalWrite(pinDir[1], HIGH);
digitalWrite(pinPwm[1], HIGH);
f = false;
b = true;
l = false;
r = false;
break;
case 108 ://l -> left
Serial.println("*** Left ***");
digitalWrite(pinDir[2], LOW);
digitalWrite(pinPwm[2], HIGH);
f = false;
b = false;
l = true;
r = false;
break;
case 114 ://r -> right
Serial.println("*** Right ***");
digitalWrite(pinDir[0], LOW);
digitalWrite(pinPwm[0], HIGH);
f = false;
b = false;
l = false;
r = true;
break;
case 82 : //R->RESET
Serial.println("*** Resetting ***");
for (int i=0; i < 3; i++){
//Setting all PWM's to LOW
digitalWrite(pinPwm[i], LOW);
}//end of for
f = false;
b = false;
l = false;
r = false;
break;
}//end of switch
}
}//end of commandCenter
int angleCount;
void readFromEncoder(){
int A;
int B;
A = digitalRead(pinEncA[1]);
B = digitalRead(pinEncB[1]);
digitalWrite(13, A);
if ( (A==LOW) && (B==LOW) )
cycleCounter = 0;
else if ( (A==LOW) && (B==HIGH) )
cycleCounter = 1;
else if ( (A==HIGH) && (B==HIGH) )
cycleCounter = 2;
else if ( (A==HIGH) && (B==LOW) )
cycleCounter = 3;
switch(cycleCounter)
{
case 0:
if ( cycleCounterOld == 1)
angleCount--;
else if ( cycleCounterOld == 3){
angleCount++;
Serial.print("cycle: ");
Serial.println(cycle);
cycle--;
}
else if ( cycleCounterOld == 2){
Serial.println("Error reading from Encoder");
Serial.println("cycleCounter");
Serial.println(cycleCounter);
Serial.println("cycleCounterOld");
Serial.println(cycleCounterOld);
}
break;
case 1:
if ( cycleCounterOld == 2)
angleCount--;
else if ( cycleCounterOld == 0)
angleCount++;
else if ( cycleCounterOld == 3){
Serial.println("Error reading from Encoder");
Serial.println("cycleCounter");
Serial.println(cycleCounter);
Serial.println("cycleCounterOld");
Serial.println(cycleCounterOld);
}
break;
case 2:
if ( cycleCounterOld == 3)
angleCount--;
else if ( cycleCounterOld == 1)
angleCount++;
else if ( cycleCounterOld == 0){
Serial.println("Error reading from Encoder");
Serial.println("cycleCounter");
Serial.println(cycleCounter);
Serial.println("cycleCounterOld");
Serial.println(cycleCounterOld);
}
break;
case 3:
if ( cycleCounterOld == 0){
angleCount--;
Serial.print("cycle: ");
Serial.println(cycle);
cycle++;
}
else if ( cycleCounterOld == 2)
angleCount++;
else if ( cycleCounterOld == 1){
Serial.println("Error reading from Encoder");
Serial.println("cycleCounter");
Serial.println(cycleCounter);
Serial.println("cycleCounterOld");
Serial.println(cycleCounterOld);
}
break;
}
cycleCounterOld = cycleCounter;
}
The plan a head is to make a complete Arduino code that monitors all three motors and connect it to a Java code. Java code can communicate with Arudino through serial communication and monitors all the three motors, being able to report the current cycle that the motor is right now at.
External interrupts in Arduino & its limitations
Description
Specifies a function to call when an external interrupt occurs. Replaces any previous function that was attached to the interrupt. Most Arduino boards have two external interrupts: numbers 0 (on digital pin 2) and 1 (on digital pin 3). The Arduino Mega has an additional four: numbers 2 (pin 21), 3 (pin 20), 4 (pin 19), and 5 (pin 18).
Parameters
interrupt: the number of the interrupt (int)
function: the function to call when the interrupt occurs; this function must take no parameters and return nothing. This function is sometimes referred to as an interrupt service routine.
mode defines when the interrupt should be triggered. Four contstants are predefined as valid values:
- LOW to trigger the interrupt whenever the pin is low,
- CHANGE to trigger the interrupt whenever the pin changes value
- RISING to trigger when the pin goes from low to high,
- FALLING for when the pin goes from high to low.
Returns
none
Example
int pin = 13;
volatile int state = LOW;
void setup()
{
pinMode(pin, OUTPUT);
attachInterrupt(0, blink, CHANGE);
}
void loop()
{
digitalWrite(pin, state);
}
void blink()
{
state = !state;}
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)